Cauda Equina Syndrome Mri With Or Without Contrast
Cauda equina syndrome mri with or without contrast. Arnold Chiari Malformation No MRI Brain Without Bells Palsy Yes MRI Brain With and Without Brain Tumor Yes MRI Brain With and Without Cancer Any Type Yes MRI Brain With and Without. The diagnostic tool of choice for cauda equina syndrome is an MRI scan. Bladder volume scanning can be useful for detecting urinary retention.
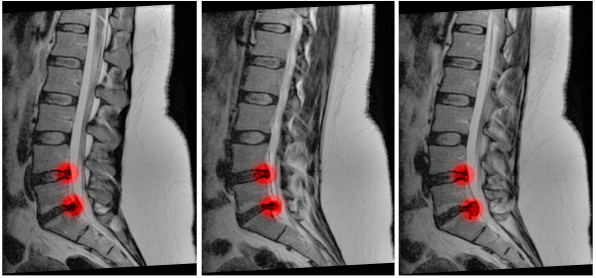
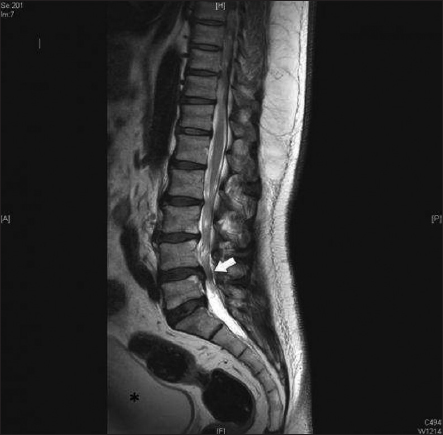
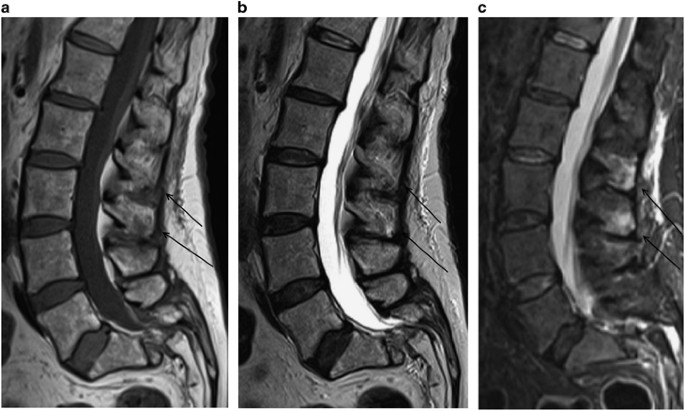
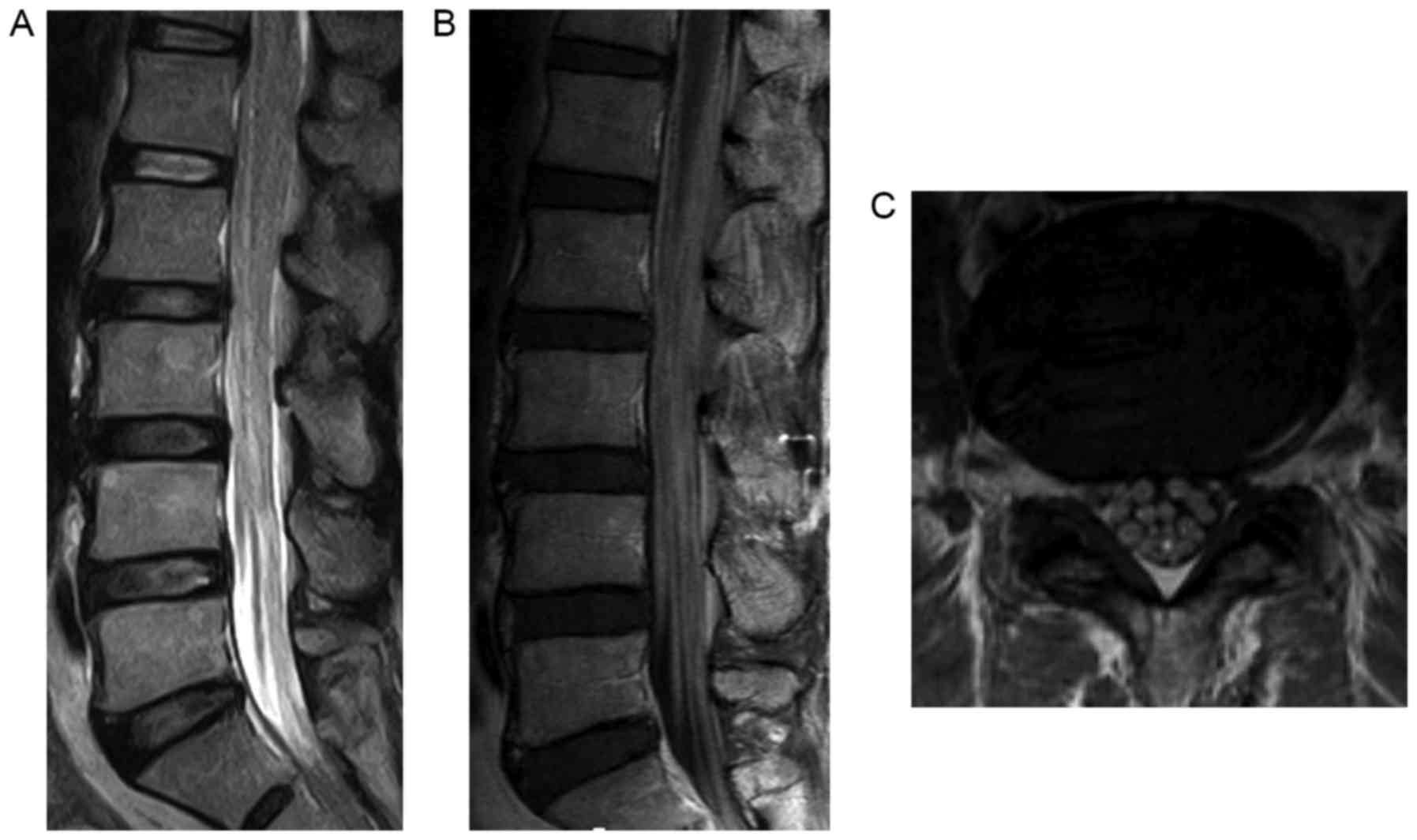
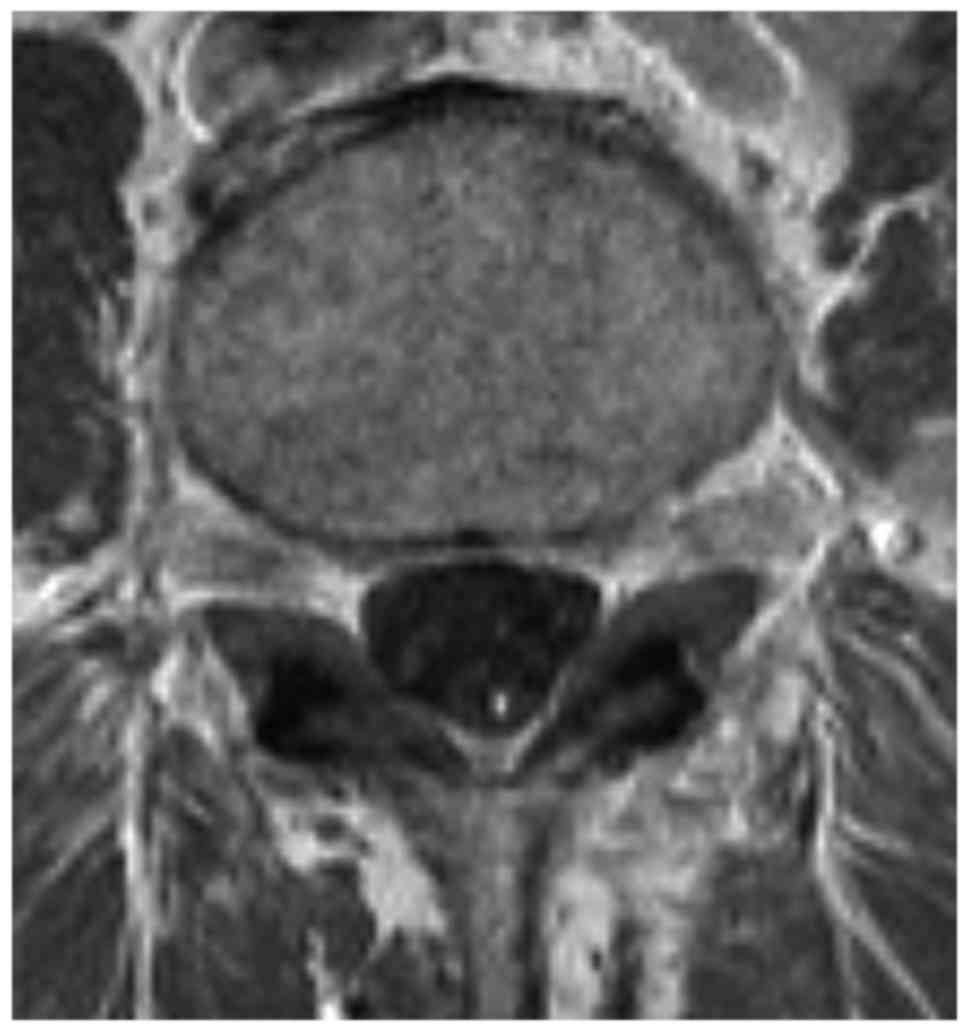
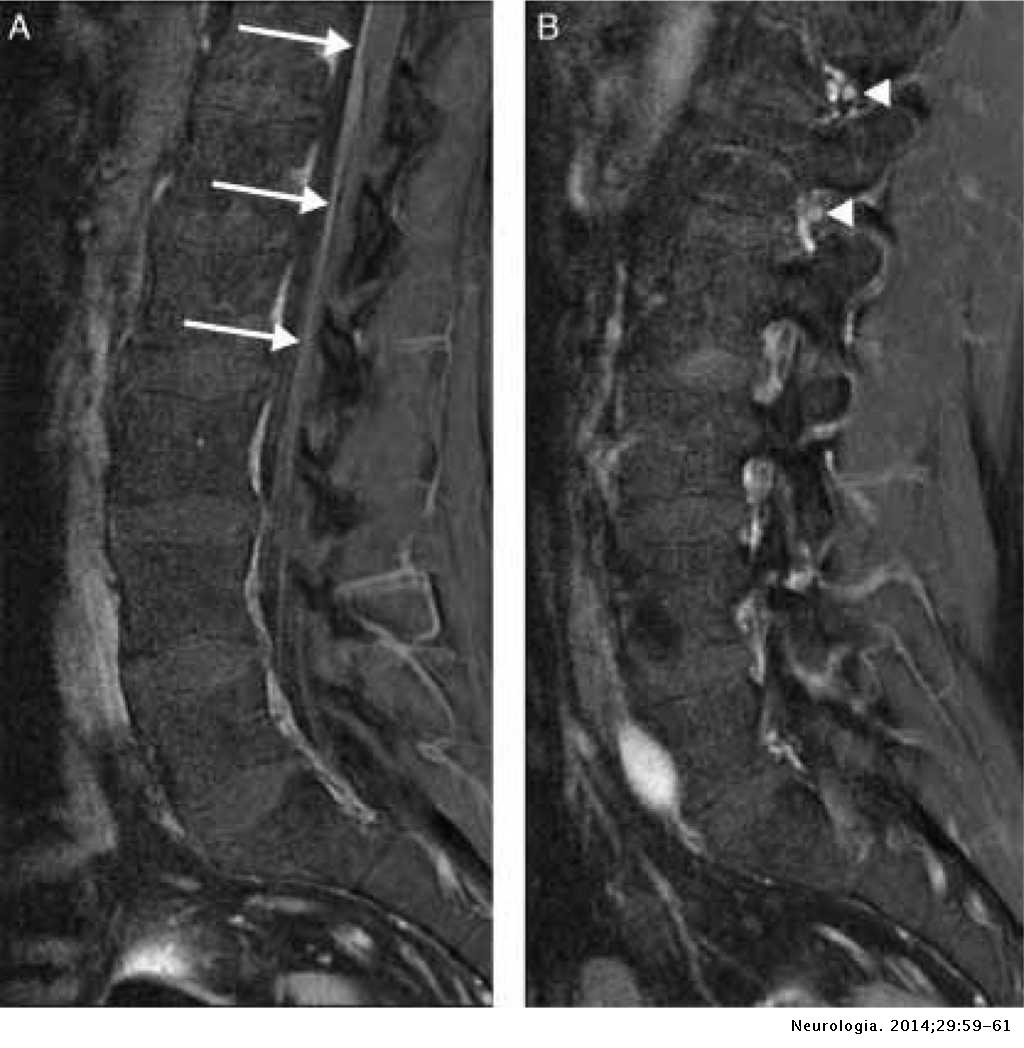
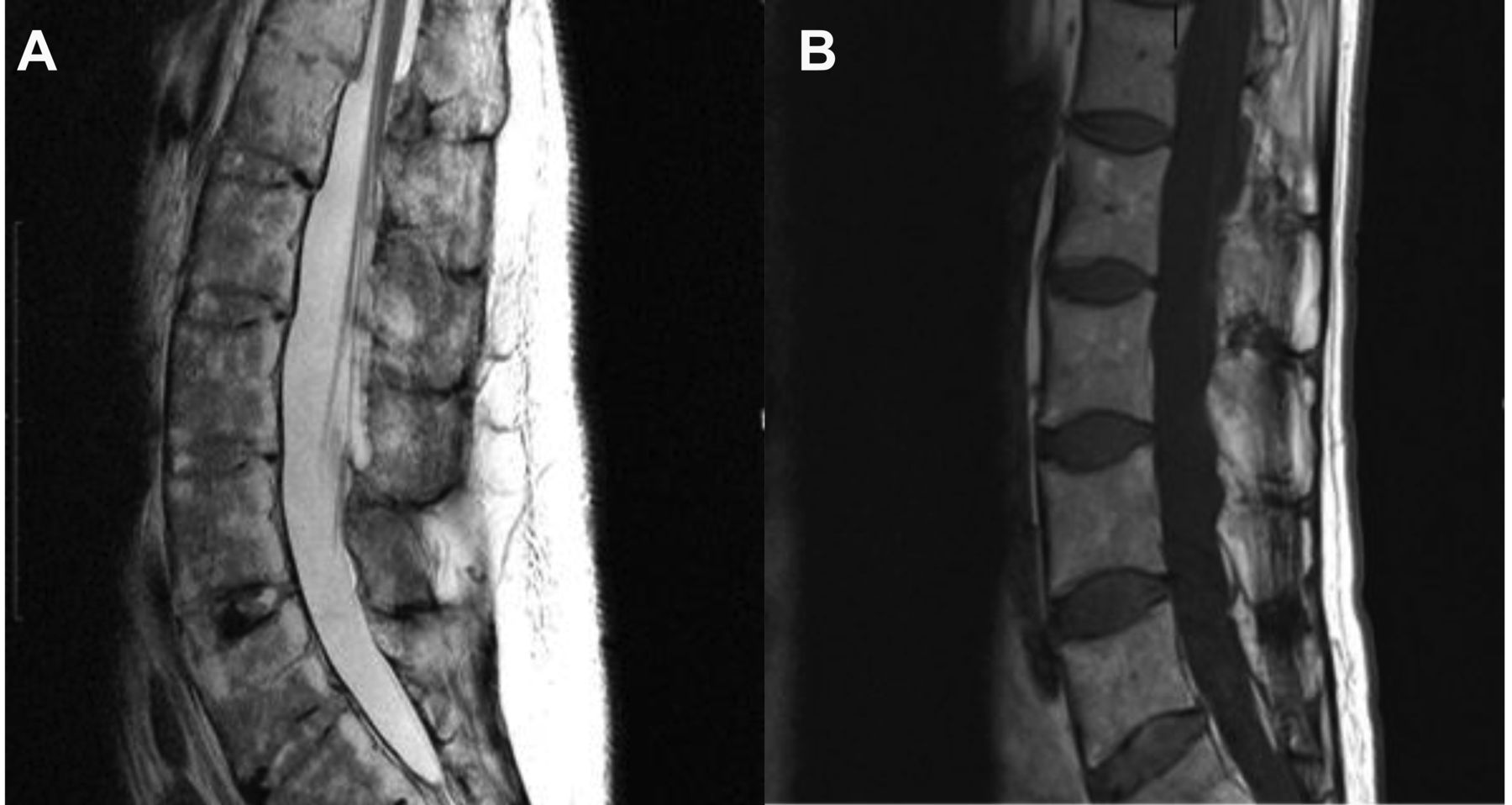
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI scan is essential to rule out cauda equina as no single or collective features will definitely confirm or exclude diagnosis. An MRI scan should either be performed on an urgent basis or an emergency basis depending upon the clinical situation. By contrast a cross sectional MRI view at L5S1 in a patient without cauda equina syndrome showing an unobstructed vertebral canal arrows from top down.
Cauda equina syndrome CES is a rare condition with a disproportionately high medico-legal profile. This portion of the spinal cord ends at the lower back and individual nerve roots at the end of the cord continue along the spinal canal and provide motor and sensory functions in the legs and bladder. Patients with this syndrome are often admitted to the hospital as a medical emergency.
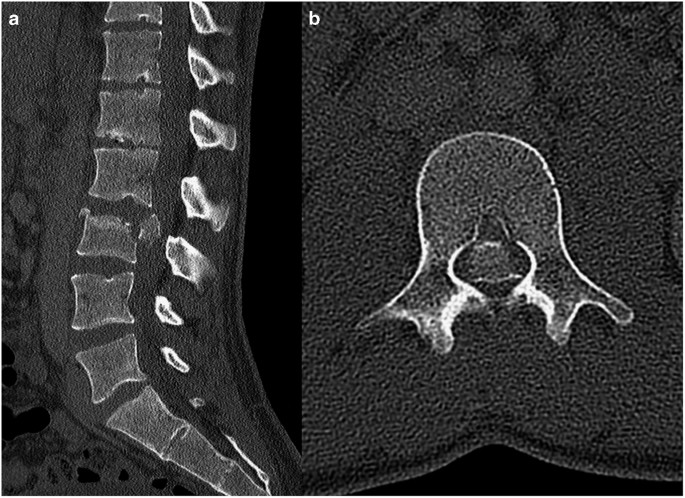
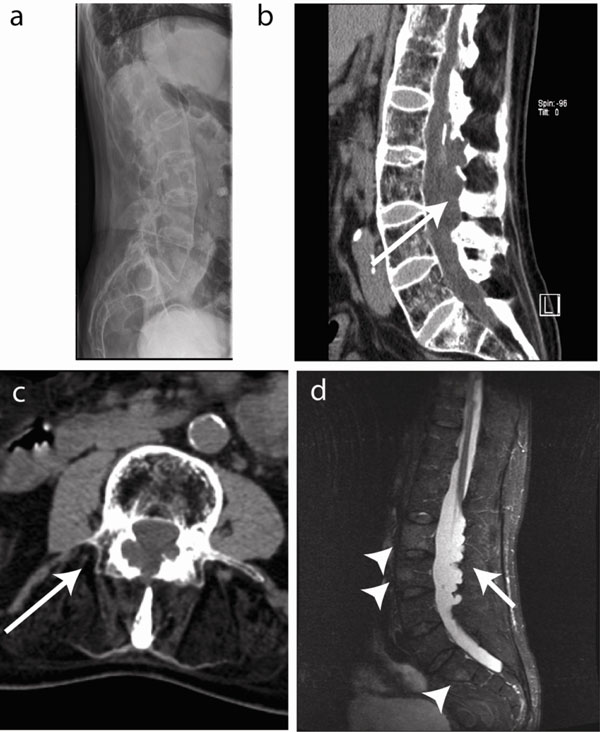
Using MR imaging as the reference standard we performed statistical analysis to determine the accuracy of CT in predicting significant spinal stenosis percentage thecal sac effacement 50 and cauda equina impingement. Previous guidelines have suggested that imaging be performed. If a patient is thought to be in the first stage of the condition called incomplete cauda equina syndrome then the MRI scan is an emergency.
Cauda equina syndrome or other severe neurologic condition. It occurs most frequently following a large central lumbar disc herniation prolapse or sequestration. The British Association of Spine Surgeons BASS emphasized that an urgent MRI scan should be performed for suspected CES and decompressive surgery should be undertaken at the earliest.
High-fi eld strength MR magnets 15 T allow evaluation of the nerves their size enhancement and involvement by a path-ologic process. MRI scan for cauda equina syndrome. A patient should therefore be sent for an emergency MRI scan meaning within around four hours of presenting to hospital.
The presence or absence of cauda equina impingement was determined on MR imaging. Of a patient with cauda equina syndrome showing a large irregular disc herniation arrow occupying most of the vertebral canal.
CES can lead to incontinence and even permanent paralysis.
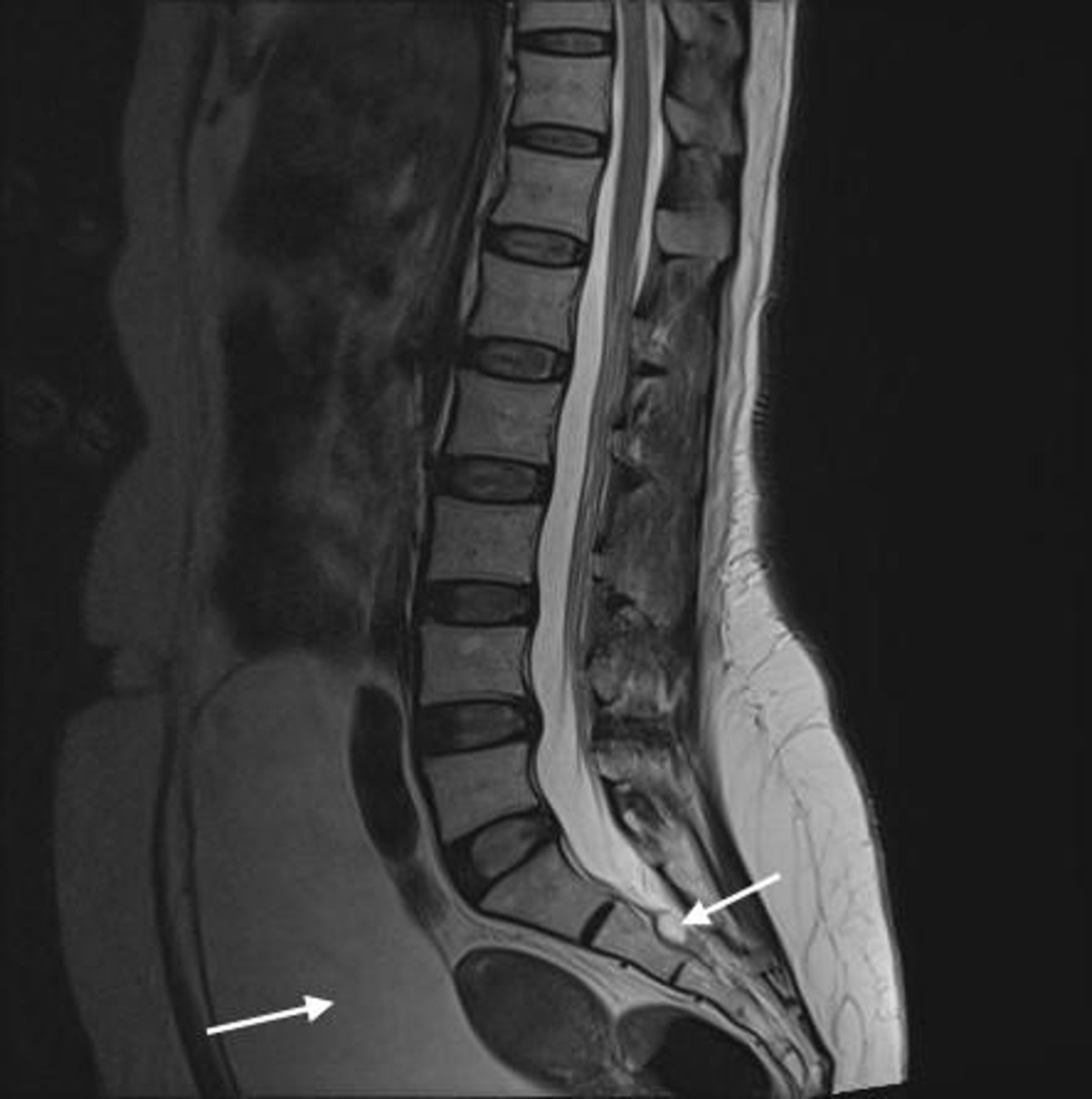
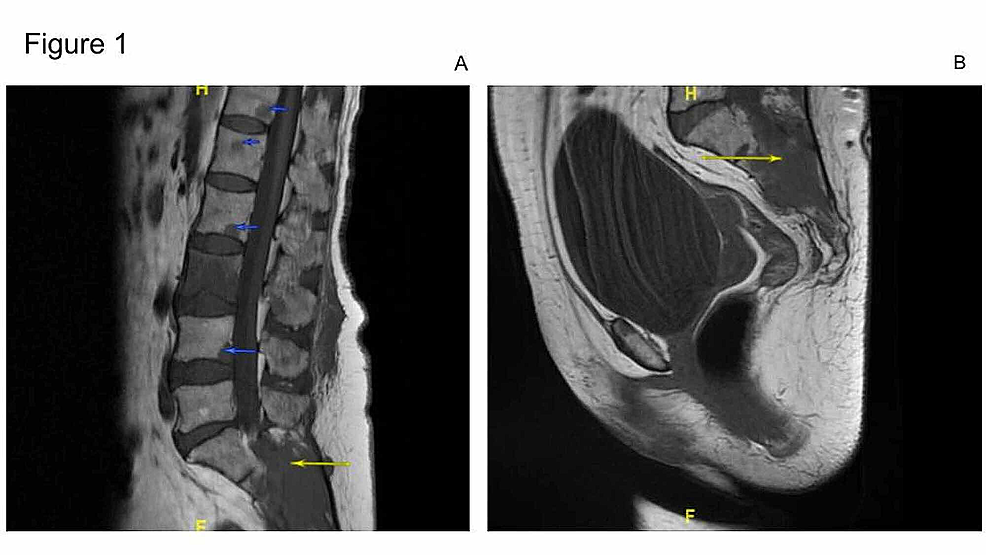
The cauda equina nerve roots send signals from the lower limbs. Pathology of the cauda equina can arise from a nerve root pia mater or arachnoid space. Cauda equina syndrome CES is a rare condition with a disproportionately high medico-legal profile. If a patient is thought to be in the first stage of the condition called incomplete cauda equina syndrome then the MRI scan is an emergency. Previous guidelines have suggested that imaging be performed. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI scan is essential to rule out cauda equina as no single or collective features will definitely confirm or exclude diagnosis. However a normal bladder scan does not exclude cauda equina syndrome and this occurs in 40-60 of cases. Vertebral canal containing cauda. This portion of the spinal cord ends at the lower back and individual nerve roots at the end of the cord continue along the spinal canal and provide motor and sensory functions in the legs and bladder.
The cauda equina nerve roots send signals from the lower limbs. By contrast a cross sectional MRI view at L5S1 in a patient without cauda equina syndrome showing an unobstructed vertebral canal arrows from top down. Cauda equina syndrome CES occurs when the nerve roots of the cauda equina are compressed and disrupt motor and sensory function to the lower extremities and bladder. Pathology of the cauda equina can arise from a nerve root pia mater or arachnoid space. Usually Not Appropriate O Bone scan whole body with SPECT or. Bladder volume scanning can be useful for detecting urinary retention. In the correct clinical context cauda equina syndrome cannot be discounted without MRI imaging ruling out cauda equina compression.


























Posting Komentar untuk "Cauda Equina Syndrome Mri With Or Without Contrast"